Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by the
progressive formation in the brain of insoluble amyloid plaques and
vascular deposits consisting of the 4-kD amyloid b-peptide (Ab).
Ab
generation is initiated by proteolytic cleavage of the amyloid precursor
protein (APP) at the N-terminal of Ab by b-secretase. The
Ab peptide is then released by proteolytic cleavage at
its C-terminus by 8-secretase. Because
both these proteases are prime candidates for therapeutic intervention, an
intense search has been underway to identify these two enzymes.
b-secretase is a transmembrane aspartic–protease
(Asp2), referred to as BACE or memapsin 2, has been characterized and
shown to have all the properties of b-secretase. Four
groups in all have now confirmed that BACE (or memapsin 2) is a convincing
candidate for b-secretase.
A goat antiserum to a synthetic peptide that
corresponds to amino acids 485-501 of the C-terminus of the human BACE is
currently available. This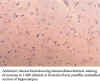 antiserum has been shown to be immunoreactive
with the unconjugated immunizing peptide by ELISA.
It can be used to immunolabel neurons in formalin-fixed,
paraffin-embedded sections of AD brain.
This antiserum is also suitable for western blots and will identify
the 70 kD glycosylated form of the enzyme.
This antibody should be a valuable tool for scientists working to
understand the role of b-secretase
in AD and how to inhibit its acitivity.
antiserum has been shown to be immunoreactive
with the unconjugated immunizing peptide by ELISA.
It can be used to immunolabel neurons in formalin-fixed,
paraffin-embedded sections of AD brain.
This antiserum is also suitable for western blots and will identify
the 70 kD glycosylated form of the enzyme.
This antibody should be a valuable tool for scientists working to
understand the role of b-secretase
in AD and how to inhibit its acitivity.
This
antiserum was produced using proprietary methodology whereby the peptide
is attached to a carrier that elicits minimal immunoreactivity so that the
antiserum has a higher degree of specificity for the peptide.
Since there is no overwhelming production of interfering antibodies
to the carrier, this antiserum can routinely be used without further
purification. Pseud-Immune™ control
immune serum (Cat no. GPA018E) from a mock immunized animal is available
to be used in conjunction with this antibody as well as the immunizing
peptide (Cat no. HSP019C), which can be used to neutralize
immunoreactivity.
Manufacturing
Reference:
Vassar, R., et
al. Science 286:735-741, 1999.
 Polyclonal Anti-human
Polyclonal Anti-human