Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46) is located exclusively in
the brain and represents a new cytochrome P450 subfamily.
This enzyme is located in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons
and converts cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol, a polar metabolite
capable of crossing the blood brain barrier and entering the
circulation. This movement
of cholesterol metabolites across the blood brain barrier is important
in maintaining cholesterol homeostasis in the brain as it has been shown
that the rate of oxidation of cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol is
similar to the rate of cholesterol synthesis in the brain.
Evidence is accumulating that indicates there is a link between cholesterol
metabolism in the brain and susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease
(AD). Studies have shown
that brains of advanced AD patients contain less 24S-hydroxycholesterol
than normal aged controls. When
the amounts and distribution of CYP46 levels were measured in autopsied
brain, there was a reduction of CYP46 levels in the neurons of the
frontal cortex of AD patients compared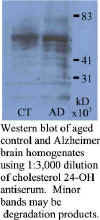 to controls. Surprisingly,
CYP46 activity was detected in the glial cells of the AD patients, but
not the controls. Since
cholesterol levels appear to affect the deposition of amyloid β-protein
(Aβ), reduced neuronal levels of CYP46 may lead to reduced cholesterol
levels, which in turn promote the formation of aggregated Aβ.
to controls. Surprisingly,
CYP46 activity was detected in the glial cells of the AD patients, but
not the controls. Since
cholesterol levels appear to affect the deposition of amyloid β-protein
(Aβ), reduced neuronal levels of CYP46 may lead to reduced cholesterol
levels, which in turn promote the formation of aggregated Aβ.
A goat antiserum to a synthetic peptide that corresponds to
amino acids 254-270 of the C-terminus of the human cholesterol
24-hydroxylase protein is currently available. This antiserum has been
shown to be immunoreactive with the unconjugated immunizing peptide by
ELISA and recognizes the ~ 58 kD CYP46 protein in western blotted brain
samples. This antibody should be a valuable tool for scientists working
to understand the role of CYP46 in Alzheimer’s and other neurological
diseases.
An
immunizing peptide (Cat no. HSP043C) is available which can be used to
neutralize immunoreactivity.
Manufacturing
Reference:
Lund, E.G., et al.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:7238-7243, 1999.