Neuroketals and
neuroprostanes are a class of compounds that result from the oxidation
of docosahexenoic acid (DHA), which is enriched in the brain and retina,
especially the synaptic membranes and retina.
DHA is a membrane polyunsaturated fatty acid that is especially
vulnerable to free radical attack because hydrogen radicals easily
remove its double bonds. The
DHA is oxidized to isoprostane-like compounds called neuroprostanes,
which can dehydrate to form highly reactive A4/J4 neuroprostanes .
Neuroprostanes can also undergo rearrangement to form D- and
E-ring neuroprostanes. These reactive neuroprostanes are called neuroketals because DHA is so
concentrated in the nervous system.
The fact that DHA is
prone to free radical attack and free radicals has been implicated in a
number of neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimerís, Parkinsonís,
Hunningtonís, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and AIDS dementia) may
make neuroketals a unique and prominent marker of oxidative injury in
the brain. The brain may
especially susceptible to oxidative injury due to its high content of
polyunsaturated fatty acids, its high oxygen consumption rate and itís
relative lack of antioxidant defenses.
NK protein adducts have been shown to occur in normal human
brain, suggesting ongoing oxidative stress in the brain.
Adduction of critical proteins by NK may be highly injurious to
neurons and may be very important in the pathogenesis of
neurodegenerative diseases associated with increased oxidative stress.
Since neuroprostanes are increased in the brains and CSF of
Alzheimerís disease patients, reactive NK formed through the
neuroprostane pathway may play a major role in oxidative brain injury.
A goat antiserum to an
oxidized DHA-conjugate is currently available. This NK antiserum has
been shown to be immunoreactive with a neuroketal/neuroprostane-modified
protein by ELISA. It has also been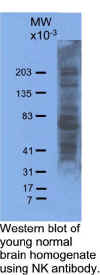 shown to detect several major and many minor human brain protein
modifications by western blot. Because
neuroketals and neuroprostanes are not species-specific, this antibody
should be applicable detect these compounds in a number of species.
This antibody should be a valuable tool for scientists working to
understand the role of neuroketal/neuroprostane modification in
neurodegenerative diseases associated with oxidative stress.
shown to detect several major and many minor human brain protein
modifications by western blot. Because
neuroketals and neuroprostanes are not species-specific, this antibody
should be applicable detect these compounds in a number of species.
This antibody should be a valuable tool for scientists working to
understand the role of neuroketal/neuroprostane modification in
neurodegenerative diseases associated with oxidative stress.
A
neuroketal-BSA conjugate is available as a positive control (Cat no.
HMP046H) which can also be used to neutralize immunoreactivity.
Manufacturing
Reference: Sparkman, D.R. and Sparkman, B.A. (2003)
Presentation at the annual meeting for the Society for Neuroscience in
New Orleans.
VIEW
POSTER